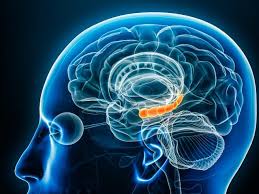
Bi-direzionale. Così potremmo definire la comunicazione tra il cervello e l’intestino, ovvero tra i due cervelli: uno in testa l’altro in pancia. Michel D.Gershon, professore di Patologia e Biologia Cellulare, all’Università di Columbia (USA) – definito il padre della neurogastroenterologia
– si fece conoscere nel 1998 per un lavoro fondamentale sul controllo neuronale del comportamento gastrointestinale e sullo sviluppo del sistema nervoso enterico (ENS), nel quale sono presenti 500 milioni di neuroni capaci sia di regolare l’attività gastrointestinale sia di influenzare il benessere mentale (stress, ansia e tensioni). Gli studi precedenti avevano accertato come il microbiota influenzasse il cervello (asse intestino-cervello), ma era meno nota la capacità di quest’ultimo di indirizzare l’ecosistema microbico presente nella cavità intestinale. Una ricerca di un gruppo di scienziati della August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research di Barcellona, pubblicata sulla rivista scientifica “Nature Metabolism”, ha utilizzato metodi avanzati per verificare come specifici segnali neurali, provenienti da regioni dell’ipotalamo, potessero modificare la composizione dei batteri intestinali in tempi estremamente rapidi (da 2 a 4 ore).
Questo studio segna una svolta nel comprendere la bi-direzionalità dell’asse cervello-intestino: una linea di comunicazione che ha il suo corrispettivo, opposto a quello enterico, nell’attività cerebrale che interviene nella combinazione della flora batteria intestinale.
Avvalendosi della chemogenetica – una tecnica utilizzata nelle neuroscienze per controllare l’attività neuronale in modo selettivo e non invasivo – i ricercatori hanno potuto attivare o inibire particolari neuroni nell’ipotalamo, in particolare quelli stimolanti l’appetito o coinvolti nella percezione di sazietà. Questa manipolazione ha prodotto effetti immediati: in alcune regioni intestinali (in particolare nel duodeno), con l’attivazione, si è osservata una fioritura della diversità batterica; mentre in altre, con l’inibizione, si è ottenuto un notevole calo di certe popolazioni batteriche.
Ormoni con funzioni opposte nel metabolismo energetico – come la leptina (che segnala la sazietà) e la grelina (che segnala la fame) – sembrano coordinare la modulazione con il sistema nervoso simpatico che funge da canale per trasmettere questi segnali. In sintesi, l’ipotalamo è il centro di controllo che regola il bilanciamento di questi due ormoni: quando il corpo ha bisogno di energia, aumenta la produzione di grelina e, invece, quando ha riserve sufficienti, la leptina segnala invece la sazietà.
Il lavoro svolto dall’Istituto di Barcellona dimostra che il cervello non è solo influenzato dal microbiota intestinale, ma può anche regolare attivamente, in tempi brevissimi, la composizione di quest’ultimo, preparandolo, per esempio, ai processi digestivi successivi all’assunzione di cibo.
Questo contributo scientifico perché rivela, insomma, la bi-direzionalità della comunicazione cervello-intestino. I risultati suggeriscono che in condizioni di disfunzione metabolica – come la leptin resistenza, comune nell’obesità o, in generale, per i disturbi alimentari – il controllo neurale sul microbiota potrebbe essere compromesso, aprendo la via a potenziali interventi terapeutici mirati alla modulazione dell’ormone della fame e di quello della sazietà.
(Articolo pubblicato sul quotidiano LaRagione del 20 Maggio 2025)Bi-direzionale. Così potremmo definire la comunicazione tra il cervello e l’intestino, ovvero tra i due cervelli: uno in testa l’altro in pancia. Michel D.Gershon, professore di Patologia e Biologia Cellulare, all’Università di Columbia (USA) – definito il padre della neurogastroenterologia – si fece conoscere nel 1998 per un lavoro fondamentale sul controllo neuronale del comportamento gastrointestinale e sullo sviluppo del sistema nervoso enterico (ENS), nel quale sono presenti 500 milioni di neuroni capaci sia di regolare l’attività gastrointestinale sia di influenzare il benessere mentale (stress, ansia e tensioni).
Gli studi precedenti avevano accertato come il microbiota influenzasse il cervello (asse intestino-cervello), ma era meno nota la capacità di quest’ultimo di indirizzare l’ecosistema microbico presente nella cavità intestinale. Una ricerca di un gruppo di scienziati della August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research di Barcellona, pubblicata sulla rivista scientifica “Nature Metabolism”, ha utilizzato metodi avanzati per verificare come specifici segnali neurali, provenienti da regioni dell’ipotalamo, potessero modificare la composizione dei batteri intestinali in tempi estremamente rapidi (da 2 a 4 ore).
Questo studio segna una svolta nel comprendere la bi-direzionalità dell’asse cervello-intestino: una linea di comunicazione che ha il suo corrispettivo, opposto a quello enterico, nell’attività cerebrale che interviene nella combinazione della flora batteria intestinale.
Avvalendosi della chemogenetica – una tecnica utilizzata nelle neuroscienze per controllare l’attività neuronale in modo selettivo e non invasivo – i ricercatori hanno potuto attivare o inibire particolari neuroni nell’ipotalamo, in particolare quelli stimolanti l’appetito o coinvolti nella percezione di sazietà. Questa manipolazione ha prodotto effetti immediati: in alcune regioni intestinali (in particolare nel duodeno), con l’attivazione, si è osservata una fioritura della diversità batterica; mentre in altre, con l’inibizione, si è ottenuto un notevole calo di certe popolazioni batteriche.
Ormoni con funzioni opposte nel metabolismo energetico – come la leptina (che segnala la sazietà) e la grelina (che segnala la fame) – sembrano coordinare la modulazione con il sistema nervoso simpatico che funge da canale per trasmettere questi segnali. In sintesi, l’ipotalamo è il centro di controllo che regola il bilanciamento di questi due ormoni: quando il corpo ha bisogno di energia, aumenta la produzione di grelina e, invece, quando ha riserve sufficienti, la leptina segnala invece la sazietà.
Il lavoro svolto dall’Istituto di Barcellona dimostra che il cervello non è solo influenzato dal microbiota intestinale, ma può anche regolare attivamente, in tempi brevissimi, la composizione di quest’ultimo, preparandolo, per esempio, ai processi digestivi successivi all’assunzione di cibo.
Questo contributo scientifico perché rivela, insomma, la bi-direzionalità della comunicazione cervello-intestino. I risultati suggeriscono che in condizioni di disfunzione metabolica – come la leptin resistenza, comune nell’obesità o, in generale, per i disturbi alimentari – il controllo neurale sul microbiota potrebbe essere compromesso, aprendo la via a potenziali interventi terapeutici mirati alla modulazione dell’ormone della fame e di quello della sazietà

Some really nice stuff on this internet site, I like it.
Merely wanna remark on few general things, The website design is perfect, the articles is very wonderful : D.
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
Hello. fantastic job. I did not anticipate this. This is a splendid story. Thanks!
I got what you mean , thanks for putting up.Woh I am glad to find this website through google.
of course like your website but you have to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth nevertheless I will definitely come back again.
I have been exploring for a little for any high-quality articles or weblog posts on this kind of house . Exploring in Yahoo I eventually stumbled upon this web site. Reading this information So i¦m satisfied to exhibit that I have an incredibly just right uncanny feeling I discovered exactly what I needed. I most definitely will make sure to don¦t overlook this site and provides it a look on a constant basis.
Thank you for sharing with us, I think this website genuinely stands out : D.
I?¦ve been exploring for a little for any high quality articles or blog posts on this kind of house . Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this website. Studying this information So i am happy to convey that I have a very good uncanny feeling I discovered exactly what I needed. I most no doubt will make sure to don?¦t fail to remember this website and give it a glance regularly.
I have been surfing on-line more than 3 hours lately, yet I by no means discovered any interesting article like yours. It is pretty price enough for me. In my view, if all webmasters and bloggers made excellent content material as you probably did, the web will be much more useful than ever before. “Nothing will come of nothing.” by William Shakespeare.
I love your writing style really enjoying this internet site.
There is apparently a lot to realize about this. I feel you made some good points in features also.
You completed certain fine points there. I did a search on the theme and found nearly all people will consent with your blog.
I just could not go away your site prior to suggesting that I actually enjoyed the usual info a person supply to your visitors? Is gonna be again regularly in order to inspect new posts
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was good. I don’t know who you are but definitely you’re going to a famous blogger if you are not already 😉 Cheers!
Some genuinely prime articles on this website , saved to fav.
This really answered my problem, thank you!
I’ve been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thank you, I¦ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your site?
Hey there, You have done an incredible job. I will certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I am confident they’ll be benefited from this website.
Wonderful blog! I found it while surfing around on Yahoo News. Do you have any tips on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Thank you
I have not checked in here for some time as I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are great quality so I guess I will add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any suggestions would be greatly appreciated.
Very interesting topic, thanks for posting.
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any suggestions would be greatly appreciated.
Oh my goodness! a tremendous article dude. Thank you Nonetheless I am experiencing challenge with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anybody getting identical rss downside? Anyone who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
It’s actually a cool and useful piece of info. I’m happy that you simply shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & assist other users like its helped me. Good job.
A person essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. This is the very first time I frequented your web page and thus far? I amazed with the research you made to make this particular publish incredible. Magnificent job!
Merely wanna remark that you have a very decent internet site, I like the style it actually stands out.
I conceive other website proprietors should take this internet site as an model, very clean and superb user pleasant layout.
Spot on with this write-up, I really think this website needs way more consideration. I’ll in all probability be once more to learn far more, thanks for that info.
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your web site and in accession capital to assert that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I will be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently rapidly.
you’ve got an excellent blog right here! would you prefer to make some invite posts on my blog?
Great line up. We will be linking to this great article on our site. Keep up the good writing.
I haven¦t checked in here for some time since I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are great quality so I guess I will add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
I genuinely enjoy studying on this site, it has got great articles. “The living is a species of the dead and not a very attractive one.” by Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche.
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I am hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
I want forgathering useful information , this post has got me even more info! .
Would love to perpetually get updated great blog! .
I’ve recently started a web site, the info you offer on this web site has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work.
Some times its a pain in the ass to read what blog owners wrote but this site is very user friendly! .
Gioca su WinShark Casino Italia! Ottieni il 100 fino a 1000 € + 50 giri gratuiti. Gioco sicuro, crypto-friendly e ricompense VIP.
Really nice style and great content, nothing else we need : D.
Some truly interesting information, well written and broadly speaking user friendly.
Hello there! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could find a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having difficulty finding one? Thanks a lot!
Wow! This can be one particular of the most useful blogs We’ve ever arrive across on this subject. Actually Excellent. I am also an expert in this topic so I can understand your hard work.
You made some nice points there. I looked on the internet for the topic and found most individuals will approve with your site.
Hey there, You’ve performed an excellent job. I’ll definitely digg it and in my opinion recommend to my friends. I am sure they will be benefited from this web site.
Some really great articles on this internet site, thanks for contribution. “When he has ceased to hear the many, he may discern the One – the inner sound which kills the outer.” by H Hahn Blavatsky.
There are some interesting points in time in this article but I don’t know if I see all of them center to heart. There is some validity but I’ll take maintain opinion until I look into it further. Good article , thanks and we would like extra! Added to FeedBurner as nicely
Goditi oltre 7.200 giochi, prelievi rapidi, bonus esclusivi e un ambiente sicuro con licenza. Registrati ora e ricevi il 100 fino a €500 + 200 giri gratis!
I?¦m no longer positive the place you’re getting your information, however good topic. I must spend a while studying more or figuring out more. Thank you for wonderful info I was looking for this information for my mission.
Goditi oltre 7.200 giochi, prelievi rapidi, bonus esclusivi e un ambiente sicuro con licenza. Registrati ora e ricevi il 100 fino a €500 + 200 giri gratis!
What i don’t realize is in fact how you’re now not actually much more well-appreciated than you may be now. You’re so intelligent. You understand thus considerably relating to this topic, produced me in my view imagine it from so many numerous angles. Its like women and men don’t seem to be interested unless it is one thing to accomplish with Girl gaga! Your own stuffs great. All the time handle it up!
I have recently started a web site, the info you provide on this web site has helped me tremendously. Thanks for all of your time & work.
Sportuna Casino Italia ▶️ Bonus di Benvenuto 500€ + 200 Free Spin ✅ 5000+ Giochi ✅ Live Casino & Scommesse Sportive ✅ Registrati ora e vinci!
Sportuna Casino Italia ▶️ Bonus di Benvenuto 500€ + 200 Free Spin ✅ 5000+ Giochi ✅ Live Casino & Scommesse Sportive ✅ Registrati ora e vinci!
NineCasino è il miglior casino online italiano con licenza AAMS. Goditi 2000+ slot, live casino, bonus fino a 1500€ + 250 free spin e pagamenti rapidi 24/7.
Servizi professionali di scrittura per tesi, tesine, articoli scientifici e progetti accademici. Qualità garantita, consegna puntuale. Contattaci ora!
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Spot on with this write-up, I truly suppose this web site needs rather more consideration. I’ll most likely be once more to read rather more, thanks for that info.
The following time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I imply, I know it was my choice to learn, but I truly thought youd have something fascinating to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about one thing that you might repair if you werent too busy in search of attention.
My spouse and I stumbled over here different page and thought I might check things out. I like what I see so i am just following you. Look forward to checking out your web page again.
hey there and thank you on your info – I’ve definitely picked up anything new from proper here. I did alternatively experience some technical issues the use of this website, since I experienced to reload the site a lot of occasions prior to I may just get it to load correctly. I have been brooding about in case your web host is OK? Not that I’m complaining, however sluggish loading cases occasions will sometimes impact your placement in google and could injury your high quality ranking if advertising and ***********|advertising|advertising|advertising and *********** with Adwords. Anyway I am adding this RSS to my e-mail and could look out for a lot extra of your respective fascinating content. Make sure you replace this once more very soon..
NineCasino Italia: bonus di benvenuto 450€ + 250 giri gratis, 5000+ giochi, cashback fino al 25, pagamenti rapidi (Visa, Mastercard, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Crypto). Guida commerciale + CTA.
Registrati su Casino Stellare e ottieni bonus fino a 2000€. Live casino, 1000+ slot, pagamenti veloci. Licenza Curacao. Gioca ora su casinostellare.live!
My brother recommended I might like this web site. He was once entirely right. This submit actually made my day. You can not consider just how a lot time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
Hey, you used to write fantastic, but the last few posts have been kinda boringK I miss your great writings. Past several posts are just a little bit out of track! come on!
Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
naturally like your website however you need to test the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very bothersome to tell the reality nevertheless I will certainly come again again.
Helping4Cancer.com is an educational resource created to share research on metabolic health, immune system support, and natural strategies that may help the body stay strong during cancer treatment and recovery. The site focuses on explaining complex topics like immune function, cellular defense, and supportive nutrition in a way that is easy to understand. Everything shared is for learning and informational purposes, giving people a place to explore research and ideas they can discuss with their healthcare team.
I do believe all the ideas you have introduced for your post. They are really convincing and will definitely work. Still, the posts are too brief for starters. May just you please lengthen them a bit from subsequent time? Thanks for the post.
I’ll right away seize your rss as I can not find your email subscription link or newsletter service. Do you have any? Kindly allow me realize in order that I could subscribe. Thanks.
Really wonderful information can be found on weblog. “Wealth may be an ancient thing, for it means power, it means leisure, it means liberty.” by James Russell Lowell.